The increasing pace of change and uncertainty in today’s global economic, geopolitical and regulatory environment has put an extreme amount of pressure on CFOs and Finance teams to lead their organizations in steering through market challenges. Yet many organizations are struggling to keep pace and many Finance teams feel stuck on a treadmill, struggling just to get access to data they can trust to report on the past, much less move the business forward.
Having modern, agile financial performance management (FPM) software and processes are critical to providing the insights needed to make informed decisions that have positive business impact. This is the focus of the 2024 BARC Score for Financial Performance Management report.
Managing Financial Performance in the Digital Age
The BARC FPM Score report focuses on the highly competitive market for FPM products and portfolios. It analyzes the strengths and challenges of 15 leading FPM software vendors that offer outstanding value to their customers. In the report, the BARC analyst team highlights the importance of effective FPM as organizations seek to continuously monitor and accurately forecast financial targets in the age of digitalization and business disruption.
Key focus areas that companies are pursuing right now in FPM include the following:
- Providing an accelerated supply of information for decision makers.
- Increasing consideration of internal and external data for decision-making.
- Greater use of data and analytics in decision-making and management processes.
- Short-term planning and forecasts with a higher updating frequency.
- Digitalization and greater software support for internal processes as an essential basis for their optimization and further automation.
According to BARC, support from modern and requirements-oriented software solutions is an essential element in achieving these goals. Hereby, the integration of various FPM disciplines in common software platforms (e.g., financial planning and forecasting, financial consolidation and close, financial reporting and disclosure management and data analytics) is a means of avoiding problems and user dissatisfaction but also helps to streamline financial management processes within companies and to drive finance transformation.
Besides the shift towards unified FPM processes and systems, the BARC analyst team also highlights the increasing demand for cloud-based deployments, self-service in finance and accounting departments as well as AI and machine learning (ML) supported decision-making capabilities in FPM software.
OneStream Recognized as a Leader
So how did OneStream fare in this evaluation? We are pleased to report that for the fourth year in a row, OneStream has been recognized as a Leader in the BARC Score for FPM software. Our Leadership position improved in the 2024 report, with OneStream now sharing the highest-rated Portfolio Capabilities and improving our placement on Market Execution. (see figure 1 below)
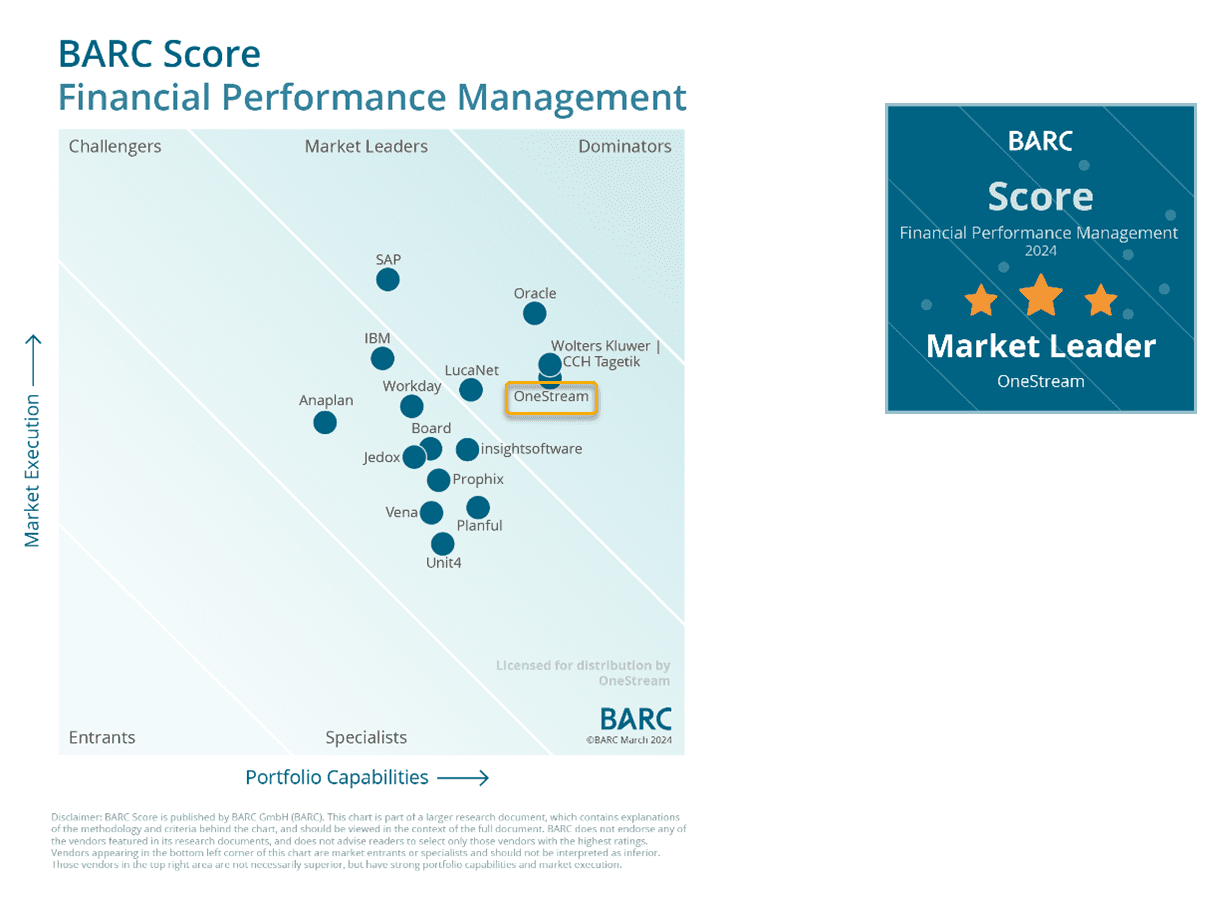
Figure 1 – BARC Score for FPM Software
Commenting on OneStream’s placement in the BARC Score for FPM, Dr. Christian Fuchs, Senior Analyst and head of Data and Analytics Research at BARC said, “OneStream is recognized as a Market Leader for its unified platform that supports the full range of CPM processes across the enterprise. OneStream can meet the needs of medium to large organizations across all industries looking for a unified and robust CPM solution.”
Here’s a look at the key strengths of OneStream that were highlighted in the report:
- Integrated CPM platform for financial consolidation and close, planning, budgeting and forecasting, reporting and analytics with built-in financial intelligence and financial data quality capabilities.
- Integrated BI and analytics functionality for (print-oriented) production reporting, financial reporting (disclosure management) with self-service dashboards and visualizations, and ad hoc analysis via Microsoft Excel add-in.
- OneStream Solution Exchange with more than 75 prebuilt business and productivity solutions that allow customers to extend the platform with additional capabilities.
- Excellent customer feedback for many important KPIs in BARC’s ‘The Planning Survey’ including customer satisfaction with vendor and product, price-to-value, and functionality. The vast majority of customers surveyed said they would recommend the platform to other organizations.
This recognition is great validation of our strategic vision and execution as it demonstrates the power of OneStream to “take finance further” with a unified CPM platform that spans a broad range of financial and operational processes. It highlights the broad range of built-in reporting and analytics functionality, including our innovation and ability to empower users with AI and ML for tasks such as predictions, scenario analyses and to automatically find insights and take action. And it recognizes our ability to meet today’s needs and adapt to future needs with our extensible platform and Solutions Exchange.
In a related report, BARC’s Financial Consolidation Survey 24, OneStream received 6 Top Ranks and 14 Leading Positions in a survey of over 500 practitioners evaluating 9 leading Financial Consolidation solutions. This report provides further validation of OneStream’s market-leading functionality and ability to address the complex requirements of the world’s largest enterprises.
Evaluating Portfolio Capabilities vs. Market Execution
To be evaluated in the BARC FPM Score, a vendor must have a strong focus on providing FPM functionality (not only analytics functionality) and supply at least four out of five following capabilities:
- Financial planning and forecasting
- Financial consolidation and close
- Financial reporting
- Ad hoc query and analysis of financial data
- Operational planning and forecasting
Every vendor is evaluated on two dimensions: Portfolio Capabilities and Market Execution. Portfolio Capabilities include functional and architectural criteria with a special emphasis on seamless integration and ease of use for business users. Market Execution focuses on factors such as product strategy, customer satisfaction, financial results and geographic coverage.
Learn More
Having modern, agile financial performance management (FPM) software and processes are critical for Finance teams to effectively steer their organizations through today’s market challenges. Over 1,400 organizations have chosen OneStream’s market-leading platform to unify and streamline critical Finance processes and deliver actionable insights across the enterprise. To learn more, download a complimentary copy of the BARC FPM Score report, and contact OneStream if your organization is ready to take Finance further and thrive in the digital age.
Learn MoreIntroduction
CFOs and Finance teams today are facing increased pressure and expectations to produce accurate and insightful reporting at speed. Why? To enable all aspects of financial management reporting and analysis required for the board of directors, equity stakeholders and functional leaders. Those requirements are especially true with Narrative Reporting and the Office of Finance.
As C-suite leaders with a bird’s eye view of corporate performance, CFOs have a strategic imperative to provide trusted insights across all aspects of the business. CFOs must also do that while driving automation, maximizing productivity and reducing risk.
A key element to that ability is being able to tell a narrative or the story behind the numbers. However, this responsibility does not fall solely on CFOs and Finance teams. That’s true even though both are the stewards of delivering trusted results for quarterly financial, budget variance and board packages with rich narratives of performance. Rather, the narrative process involves collaboration across all business leaders. Such collaboration requires not only comparing the latest results to plans and targets, but also describing both the good and the bad in context. In fact, those aspects are essential to telling the story of the latest results to the board of directors, equity stakeholders and functional leaders.
Moving Beyond the Numbers
At a recent OneStream event, moving beyond the numbers to telling the story behind the numbers, was the message from several of our customers and prospects. One Finance leader put it this way: The whole Finance profession has, for too long, focused primarily on just the numbers. While the numbers need to be accurate and trusted, the ability to look beyond just the numbers and into the why is becoming increasingly more important. How do we explain our performance and tell the story behind the numbers?
Finance is uniquely positioned to not only deliver trusted results but also facilitate the storytelling process to put numbers in context with current and future business performance. This process is Narrative Reporting, and it is a combination of people, process AND technology. So how do we unify and streamline this process in technology to help facilitate corporate storytelling?
The Narrative Reporting Challenge
Narrative Reporting is traditionally a time-consuming, complex and inefficient manual process. To tell the story behind the numbers, Finance must collect comments, assemble data and reports, and create narratives for reporting.
Yet current solutions and approaches for Narrative Reporting comprise the following:
- Multiple tools
- Duplication of data and metadata
- Cut-and-paste reports, data and comments
- Manual creation of narratives in documents, spreadsheets or separate solutions
This mix creates complexity in the assembly, review and approval of narratives and narrative reports. As a result, the process involves difficulties. How? Incorporating the collaboration needed across the business for the analysis and collecting insights from business leaders to pull together the story both become more difficult.
Ultimately, traditional approaches fall outside your CPM system (arguably your system of record for performance). Thus, Finance teams are challenged to execute the process to collect the narratives and facilitate the needed analysis. Those challenges introduce the risk of reporting errors, resulting in lack of trust in the reports, data and narratives used for financial and management reporting.
OneStream’s New Approach to Narrative Reporting
To address the challenge, OneStream is introducing a new approach to Narrative Reporting at our Connect London event on April 24, 2024. The new approach streamlines and centralizes Narrative Reporting. How? By uniquely unifying it with all consolidation, close, financial and operational planning to automate the narrative assembly, live analysis, review and reporting processes.
The approach ultimately eliminates reliance on the old approach. That means Finance no longer needs multiple solutions and tools. Nor is copying and moving data and metadata, rekeying and cutting/pasting necessary. Thus, the new approach simplifies the process and ensures context, confidence and auditability within the Narrative Reporting process.
Key Features
The new approach uniquely unifies and streamlines narrative report creation, from narrative assembly to data analysis and narrative capture. As a result, Finance leaders can leverage live OneStream data to drive transparency, confidence and contextualization behind financial data. Key features of OneStream’s new approach to Narrative Reporting include the following:
Centralize Everything
Centralize the creation of Narrative Books all in one place in OneStream, organizing all report content, live analysis and collaborative capture of narratives. Centralization ensures Finance and business leaders can analyze and communicate the story behind the corporate performance.
Live Analysis at Every Step
Contextually analyze live, validated OneStream data and report content rather than relying on static or copied data in many different solutions and tools. Live analysis streamlines the analysis, review and narrative capture process.
Collaborate and Approve with Confidence
Collaborate with comments, track changes, views of all activity, submission/approval processes and version management to reduce risk and reporting errors.
Automate Narrative Reporting Processes
Embed Narrative Reporting in the close, planning and other workflow processes with approvals to collect narratives during consolidation, close, and financial and operational planning process. This saves time, drives efficiency and collaboration, and ensures confidence in the Narrative Reporting process.
Leverage a Trusted and Familiar Interface
Leverage the same OneStream interface and trusted reporting content alongside the familiarity of Microsoft Office to capture narratives and create rich, formatted and collaborative Narrative Books. Intuitively combine rich text documents, text, Word documents, Excel sheets and PDF documents, all uniquely unified in one solution. Finance can thus easily capture narrative content and deliver formatted Narrative Books.
One of our OneStream public sector agencies previously used six different tools to build its 1,400-page budget to submit for annual budget appropriation. The agency now only uses OneStream to create all its budget books, including budget briefs, justifications and final budgets. With OneStream, the agency achieved the following:
- Streamline the budget and narrative process
- Standardize and automate the process with master templates and exhibits
- Shorten the budget change and narrative capture process from days to minutes
OneStream Narrative Reporting Availability
OneStream’s new approach to Narrative Reporting is available today and will be officially launched at our Connect London event on April 24th and highlighted at our annual Splash User Conference in Las Vegas on May 20th. Other new innovative capabilities and Solution Exchange solutions will also be unveiled.
We encourage our customers, prospects and partners to attend these events, visit our Website and check out our social media posts for more details on this new approach to Narrative Reporting.
Conclusion
Over 1,400 companies globally have made the move to OneStream’s Intelligent Finance Platform. Why? To unify consolidation, close, financial and operational planning, reporting, and analysis, to deliver confidence and trust in the results. And to move beyond the numbers to tell the story of corporate performance.
To better understand why, visit our website at www.onestream.com.
Learn MoreOur reimagined brand celebrates what’s possible when organizations have the access, insights, and capabilities they need to Take Finance Further™.
OneStream was founded on the core belief that with the right technology, organizations could take Finance beyond just reporting on past performance and towards informing and guiding business strategy and growth.
That’s why our founders – Tom, Bob, and Craig — set out to build a cloud-based platform to not only modernize the financial reporting and planning processes of the past, but also arm the Office of the CFO with the insights and capabilities to strategically steer the business to the future.
In short, OneStream is on a mission to Take Finance Further™.
This founding principle has fueled our ability to build and continually innovate the only enterprise Finance platform that:
- uniquely unifies all your financial and operational data,
- embeds AI for better decisions and productivity, and
- is infinitely extensible to meet the needs of your business today and tomorrow.
It’s also why over 1,400 of the world’s largest and most recognized brands rely on OneStream to stop wrangling data, start steering the business, and Take Finance Further.
Now it is time for our brand to catch up.
That’s why we spent the past six months researching, interviewing, and testing the OneStream brand message and identity with customers, partners, employees, and influencers – including many of you. We learned a lot about how the market views OneStream, where we add the most value, how we’re differentiated, and what our target Finance audience cares about most.
This led us to home in on the above simplified and elevated OneStream brand story. A story that cuts through the noise, sets aside the tech jargon and buzzwords, and gets down to the essence of OneStream and the unique value we deliver to the Office of the CFO.
To complement our story, we have embraced an evolved visual style that embodies the spirit of our core mission and inspires a desire to shape a better future. This includes:
- a new brandmark and symbol that simultaneously modernizes our logo while paying homage to OneStream’s original dual-S curve design, portraying continued innovation and growth — for OneStream, our customers, and our partners;
- a proprietary typography system that further amplifies our commitment to delivering efficiency and simplicity;
- a multi-color brand palette that reflects the modern and disruptive nature of the OneStream platform; and
- a photographic style that brings humanity to our story and puts the customer at the center of it.
You can get a feel for the new OneStream brand on the OneStream Brand Hub.
And now, we’re sharing our vision with the world through a global, multi-channel campaign designed to reach, engage, and inspire Finance leaders to Take Finance Further.
I encourage you to keep an eye out for OneStream in the print, digital, broadcast and outdoor channels you know and trust most. Get familiar with our story, our value, and our brand. And join us in our commitment to constantly look ahead, so our customers can succeed today and be ready for whatever comes next.
In today’s dynamic environment, government agencies are facing increased demands to effectively communicate strategic visions, initiatives and community impact. Volatile economic and financial factors, regulatory issues and technology enhancements especially all make it harder to meet those demands. No wonder looking ahead with a strategic planning process can feel daunting. Yet the right tools, processes and data analytics help agencies gain efficiencies, enable better insights and feel more confident in the future when building strategic plans.
But before we dive into 5 strategic planning tips for government agencies, let’s quickly review what strategic planning entails.
What Is Strategic Planning?
Per the Government Finance Officers Association (GFOA), strategic planning for government agencies involves articulating where or what an organization wants to be in the future. That process includes designing a vision and identifying goals and objectives. While related to developing financial policies, capital improvement planning and budgeting, the strategic plan is inherently different.
Typically, strategic planning is used to do the following:
- Articulate an organizational vision
- Foster organizational alignment
- Undertake comprehensive environmental and economic assessments
- Prioritize services, initiatives and programs
- Establish goals
Why Does Strategic Planning Matter?
Strategic planning helps Finance leaders model the organization as it exists today and then layer on possible strategies over the top. What types of strategies? Changes in tax policies, capital projects, new programs and so forth are some examples. Through this proactive approach, stakeholders can visualize plausible future scenarios and their corresponding impacts. Strategic planning can be a useful storytelling tool to help stakeholders understand the future impact agencies can have on their community within resource constraints.
Plus, internally, strategic planning is a powerful way to set the direction and prioritization of an agency. Why? The planning completes a cohesive feedback loop. First, the strategic plan drives the budget and resource allocation. Then actuals drive revisions to the forecast. And finally, forecast changes influence the strategic plan in future years (see Figure 1). This feedback loop ensures agencies are aligned on maximizing community impact.
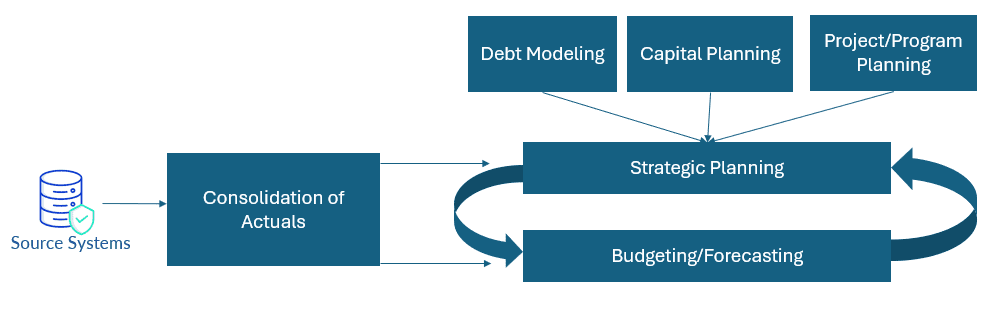
Strategic Planning Tips for Government Agencies
Getting a handle on what’s going to happen tomorrow or next week is tough on its own. So understanding what might happen in 1-2 years – or in 5 years – seems nearly impossible.
And if the planning process is happening in offline spreadsheets? Well, that’s an even bigger headache. Putting together a plan that truly represents a vision of the future requires aligning actual data with inputs from across the agency. Thus, having to combine various spreadsheets that lack data quality and consistency controls can make any planning process a tedious, time-consuming task.
But it doesn’t have to be that way! Below are 5 strategic planning tips for government agencies to save time, get better insights and gain confidence when building strategic plans.
1. Centralize data and ensure quality control.
The foundation of a reliable strategic plan lies in having accurate and timely data to support confident funding and spending decisions. In addition, the data used for the strategic plan must be consistent and aligned with the data used for other financial planning processes, including the budget.
How can alignment be created? By working with IT and operational stakeholders to leverage available data from across the organization, Finance teams generate informed insights and make data-driven decisions. Implementing tools that centralize data from multiple sources, ensure data quality control and provide transparency with drill-back capabilities ultimately fosters alignment and trust within the organization.
2. Integrate financial statements.
Organizations often focus primarily on the Statement of Activities. But modeling the Balance Sheet and Cash Flow Statement in the strategic plan also has significant value. Why? In an ideal world, agencies could have endless cash. But today Finance leaders typically have financial constraints and must prioritize and balance funding to ensure long-term financial sustainability.
By integrating all three financial statements, stakeholders can better understand the long-term financial impact of different strategies and external factors. Stakeholders can also make informed decisions that include the following:
- Utilizing recurring vs. non-recurring funds
- Using reserve allocations
- Covering core services
- Funding new initiatives in an optimized way (i.e., debt vs. cash)
3. Conduct scenario analysis.
Scenario planning helps organizations be more resilient and adaptable. The process requires identifying a range of possible future conditions and then developing plans to respond to each condition.
For example, a local agency may want to understand potential scenarios with changes in tax policies. Government agencies, after all, must carefully consider the potential impacts of tax policy changes to balance revenue needs with the economic health of the community.
Scenario planning not only improves the accuracy and effectiveness of the planning efforts, but also helps Finance become a strategic partner to the organization. By understanding possible outcomes and having a plan in place to react, agencies can be better positioned for success in a rapidly changing world.
4. Automate calculations and logic.
Excel can be highly error prone – whether due to mis-keyed or corrupted data cells or incorrect or broken formulas. Plus, Excel can especially be burdensome when data is pulled from multiple sources and each part of a spreadsheet relates to and affects other parts. Tiny errors can easily –and quickly – turn into bigger headaches.
Implementing a software solution that automatically brings data together, leverages standard calculations and easily performs wide-ranging scenarios is a game-changer for Finance teams. Gone are the days of pouring over buggy spreadsheets and digging through rows of data to fix mis-keys or errors. Instead, the right solution can restore work-life balance. How? By allowing the team to focus on research and analysis instead of spending long hours and late nights in the office dealing with data issues.
5. Utilize dashboards & visuals to tell your story.
Dashboards and visualizations are powerful storytelling tools for the strategic plan. In fact, effective dashboards help guide decision-making with a varied audience (see Figure 2). The ability to quickly visualize data trends, impacts of initiatives and economic drivers, and core financial KPIs over time becomes possible with dashboards and reports. And those capabilities enable better and faster decision-making.
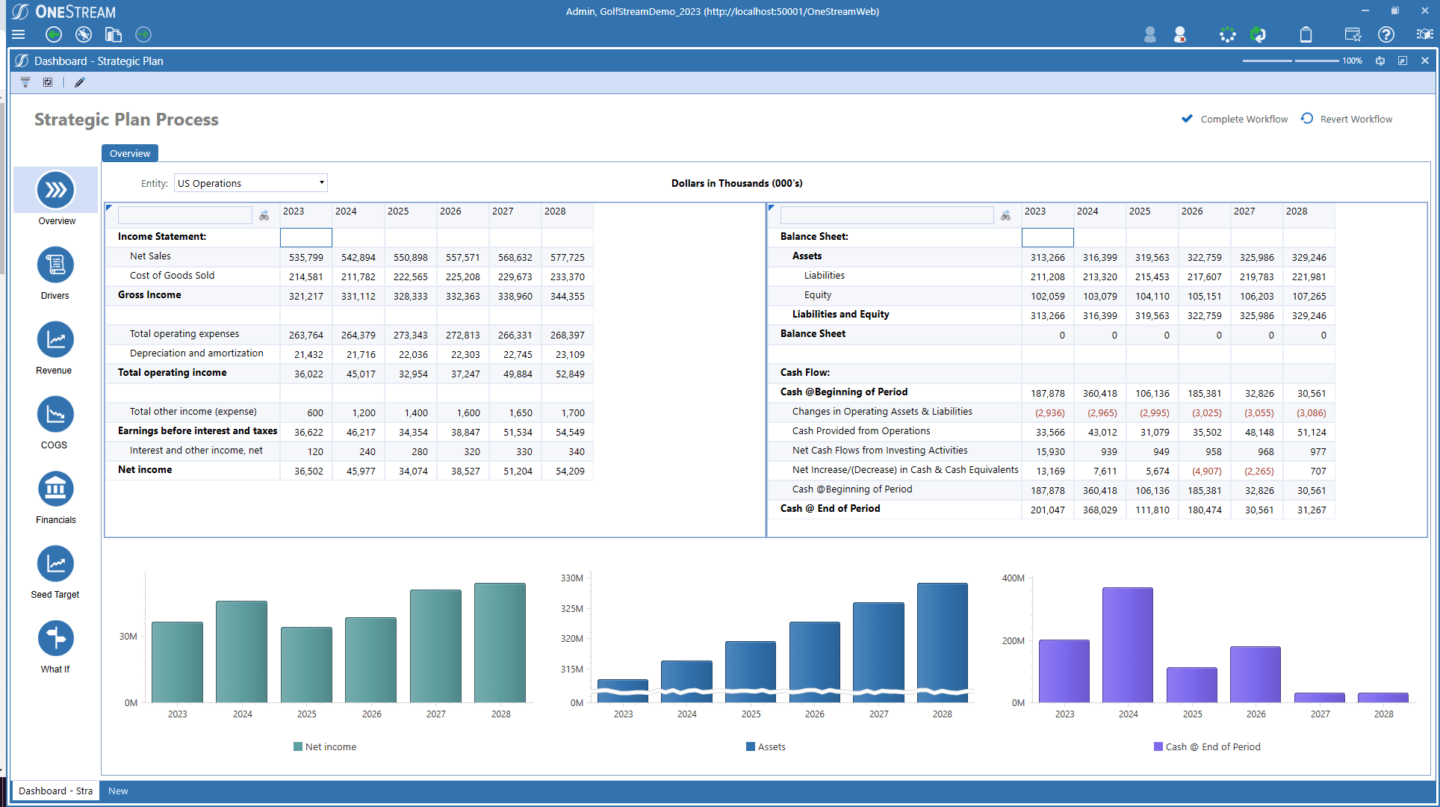
Conclusion
While predicting the future remains uncertain, strategic planning equips Finance leaders with the foresight and agility to capitalize on opportunities and navigate potential changes effectively. Finance can leverage integrated data solutions, automated calculations, scenario planning frameworks and impactful visualizations. Through those aspects, Finance teams will improve efficiency, insights and confidence in the strategic plan and position the agency for long-term success.
Learn More
OneStream brings Finance processes into a single platform solution to enable seamless integration between the data, people and processes driving the organization. Learn more about how OneStream uniquely empowers government Finance teams to enhance planning, gain new insights and streamline Finance processes.
Learn MoreIntegrated Business Planning, or IBP for short, is a strategic management process that connects various organizational departments to align business operations with financial goals. How? By integrating business functions – such as Sales, Marketing, Finance, Supply Chain and Operations – to create a holistic view of the company’s performance and future direction. This blog post offers a comprehensive guide to discuss what precisely IBP entails and how Finance can drive business results and collaboration within the organization via a robust and comprehensive IBP process.
What Is IBP?
While the business world and Finance have always had shared language and acronyms, some new (and reimagined) acronyms may now be flooding your feed. One such topic you may be hearing a lot about lately is Integrated Business Planning (IBP). Yet the concept of IBP isn’t new. In fact, it’s related to Sales & Operations Planning (S&OP), a concept that’s been around awhile.
Still, IBP may seem overwhelming in the context of all the different acronyms related to financial and operational planning floating around lately. For example, IBP, S&OP, eXtended Planning and Analysis (xP&A) and others are just a few acronyms muddying the waters. But this comprehensive guide to all things IBP aims to help demystify the process.
So what, exactly, is IBP?
IBP ultimately aims to unify business strategy with planning, budgeting and forecasting activity for all business lines and functions – providing one version of the numbers. In turn, a trusted, common view of the numbers provides a robust baseline for agile decision-making. That common view also keeps all teams collectively trying to achieve the same corporate objectives while staying focused on specific KPIs. In other words, the different teams maintain their independence while working in unison to achieve corporate success by leveraging the same trusted and governed data.
The bottom line? IBP is about aligning strategy intent, unifying planning processes and bringing the organization together.
How IBP Works
The IBP process is a framework to address the C-suite needs and help implement the business strategy and manage uncertainty to improve decision-making. So what’s the secret sauce of IBP to make all of that happen? A collaboration between the different teams under a single view of the numbers that must unequivocally be tied to financial performance. That’s how the C-suite gets value from IBP. Consequently, Finance plays a central role in the IBP process.
IBP typically focuses on horizons of 24-60 months, as opposed to the short term. That focus equates to Integrated Tactical Planning or Sales and Operations Planning and Execution. Since the process must be fully integrated, it removes the departmental silos. Plus, the IBP process must adapt to the organizational construct of every business (IBP isn’t a one-size-fits-all type of process).
A typical IBP process involves several stages:
- Data Collection and Analysis: Gathering relevant data (e.g., sales forecasts, production capacities, inventory levels and financial projections) from different departments.
- Demand Planning: Predicting future demand based on historical data, market trends, customer feedback and sales forecasts.
- Supply Planning: Determining the resources and capabilities (e.g., materials, production capacity and distribution channels) needed to meet the forecasted demand.
- Financial Planning: Developing financial plans and budgets aligned with the demand and supply forecasts, considering factors such as revenue targets, cost structures and investment requirements.
- Scenario Planning: Creating alternative scenarios to assess how different strategies, market conditions or external factors impact business outcomes.
- Management Business Review: Collaborating across departments to make informed decisions on resource allocation, investments, pricing strategies and operational adjustments.
- Execution and Monitoring: Implementing the plans, tracking performance against targets, and continuously monitoring key metrics to identify deviations and take corrective actions.
The most efficient way to foster this collaboration is through a unified solution and data model that caters to the needs of the various agents involved on each review. In fact, Figure 1 shows how one solution gathering all the capabilities in the greyed area under a unified data model is the most efficient approach to IBP.
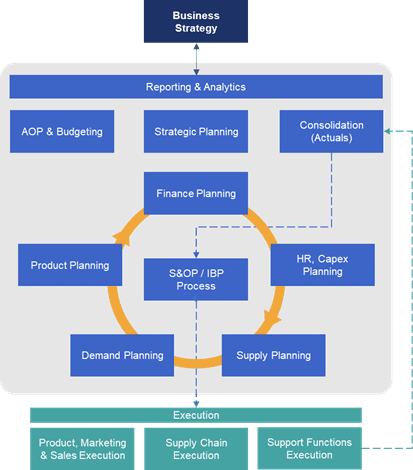
Figure 1: A Unified Data Model for IBP
Core Elements and Stages of the IBP Process
The IBP process includes the following core elements:
- Governance Structure: Establishing a cross-functional team with representatives from key departments to oversee the IBP process, define roles and responsibilities, and ensure alignment with organizational goals.
- Data Integration: Integrating data from different systems and sources to create a single source of truth for decision-making, using technologies such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, Corporate Performance Management (CPM) tools, business intelligence (BI) tools and data analytics platforms.
- Collaborative Planning: Encouraging collaboration and communication between departments to share insights, align objectives and develop consensus-based plans that support overall business objectives.
- Continuous Improvement: Implementing feedback loops, performance reviews and process refinements to enhance the effectiveness and agility of the IBP process over time.
Learn More
Want to learn how you can maximize the benefits of your IBP process and get leadership on board with the plan? Check out our eBook Unifying Integrated Business Planning Across Finance and Supply Chain. You’ll learn how to unify IBP across Finance and Supply Chain teams and read about use cases as proof points. Plus, you’ll gain an understanding of the unique capabilities OneStream’s Intelligent Finance Platform brings to unify Finance and Supply Chain planning activities.
Learn MoreAs economic volatility keeps rising in frequency and magnitude, Financial Planning & Analysis (FP&A) teams are facing unprecedented pressure. Traditional quarterly or annual budgeting is becoming obsolete, unable to keep pace with rapid changes – rendering static budgets irrelevant. Additionally, exponential growth in data sources and volume requires extensive data transfer, reconciliation and consolidation processes before insights can inform budgets, forecasts or plans. But business planners are in luck. Why? Several use cases of AI in enterprise Finance enable faster data processing, increased forecast accuracy and deeper insights.
Rapidly becoming essential for all enterprises, AI ultimately streamlines processes, unlocks valuable insights and drives strategic decision-making. Soon, AI will be embedded across all enterprise Finance processes. This blog post therefore explores 3 use cases of AI in enterprise Finance, setting the stage for a deeper dive into OneStream’s innovative Sensible Machine Learning solution.
3 Use Cases of AI in Enterprise Finance
Incorporating AI into FP&A is fundamentally reshaping how organizations forecast, budget and make strategic decisions. To show why, let’s explore 3 transformative use cases of AI in enterprise Finance:
1. Predictive Forecasting
Predictive forecasting is a cornerstone of FP&A, enabling organizations to anticipate future financial performance and make informed decisions. AI-driven predictive analytics offers a paradigm shift in forecasting accuracy and reliability. How? By leveraging advanced algorithms to analyze historical data and market trends, identify patterns, and accurately predict future financial outcomes. These predictive models provide valuable insights into cash flow management, revenue projections and expenditure planning.
As a result, Finance professionals are empowered to allocate resources efficiently and optimize financial performance.
2. Automated Forecasting and Planning
Traditionally, forecasting and planning processes have been time-consuming and labor-intensive tasks for FP&A teams. But not anymore. AI automation streamlines these processes by automating routine tasks, optimizing resource allocation, and improving the accuracy and agility of forecasting and planning activities. With purpose-built AI solutions, Finance can automate mundane financial processes (e.g., data entry, forecast creation and reconciliation). And that leaves more time for value-added activities.
By integrating AI-driven automation tools into workflows, enterprises can thus accelerate decision-making processes, improve data accuracy and achieve cost savings.
3. Financial Performance Analysis
Financial performance analysis is a critical function within FP&A. Why? Such analysis enables organizations to gain deeper insights into the drivers impacting business operations and profitability. Through embedded AI, such analysis becomes even more insightful and actionable by uncovering hidden patterns and relationships within financial, operational and external data.
Traditional analysis methods, on the other hand, may struggle to identify subtle correlations or complex interactions among the various factors influencing financial performance. But AI algorithms excel at processing large volumes of data and detecting nonlinear relationships that may not be immediately apparent to human analysts.
By analyzing diverse data sources (e.g., financial statements, operational metrics, market trends and macroeconomic factors), AI reveals nuanced insights into the drivers shaping financial performance. Finance professionals can now use these insights to steer the business and stay ahead of the competition.

As Finance continues to embrace AI, a practical and sensible ML approach – one that balances automation with transparency and human insight – has become increasingly important. Effective planning is, after all, critical for businesses to remain competitive and adapt to changing market conditions.
At OneStream, we call this Sensible ML.
Introducing Sensible ML
OneStream’s Sensible ML (see Figure 1) – which is purpose-built for FP&A – is a paradigm shift in leveraging AI for Finance professionals. By seamlessly unifying AI within an enterprise Finance platform, Sensible ML creates thousands of forecasts and insights previously impossible with manual processes.
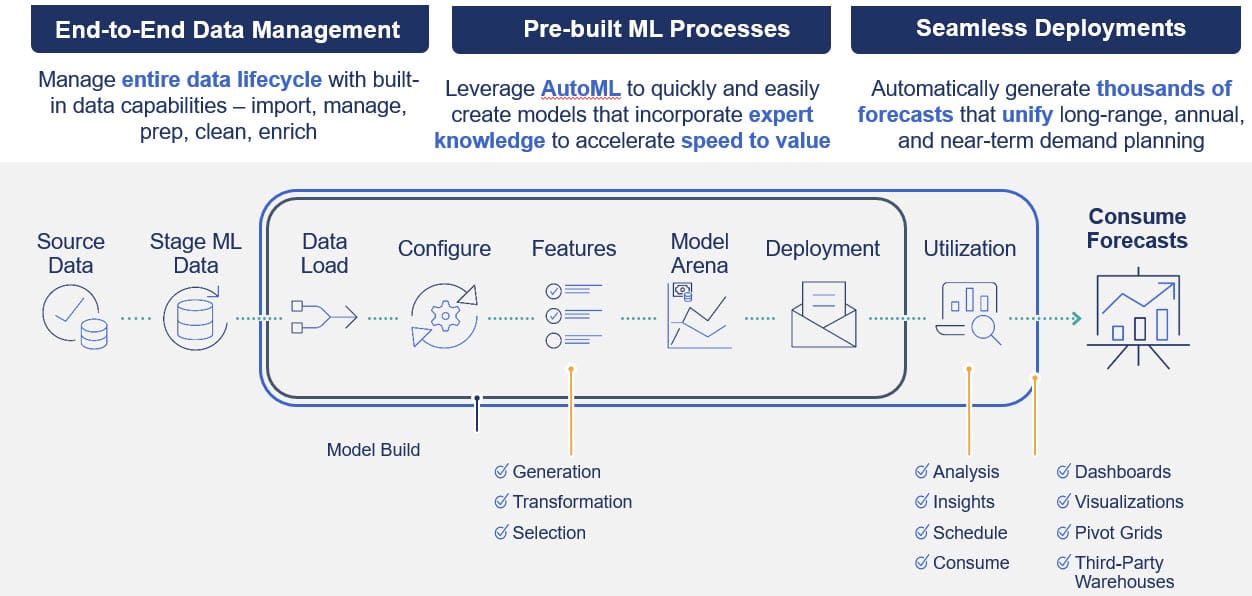
Figure 1: Sensible ML Process Flow
Purpose-Built AI for FP&A in a Unified Platform
By integrating AI, Finance teams can seamlessly leverage AI capabilities without having separate tools, systems or teams. No longer are the days of having data scientists create a forecast without understanding the business value. Also gone are the days the Finance team receives the output with no understanding of where the numbers originated.
Instead, with purpose-built AI for Finance and Operations, business planners are independently creating ML-backed forecasts. And these planners are doing so for the entire ML-forecasting process – from data ingestion and quality to model building, all the way to utilization and consumption. As a result, Finance professionals can now explain their accurate forecasts with confidence and at scale across hundreds or thousands of forecasts.
Sensible ML also incorporates external factors (e.g., weather, macroeconomic factors) to create highly accurate forecasts and utilizes a unique, groundbreaking concept: the Model Arena.
The Model Arena offers tailored precision by automatically selecting the most performant model for each forecasted line item. In contrast, the one-size-fits-all approach applies a single model for all forecasted line items, failing to account for the characteristics of each product-location combination. The Model Arena approach instead produces a much higher level of accuracy by accounting for the nuances of different forecasted products by locations.
Polaris, a global leader in powersports whose products have vastly different characteristics, offers a good example of the power of Sensible ML. Why? With Sensible ML, Polaris can now forecast for specific products and locations with distinct models across the business. Only a unique ML model tailored for Polaris snowmobiles or off-road vehicles can create an accurate sales forecast. In turn, Polaris can optimize for downstream processes (e.g., resource allocation) or maximize the contribution margin.

Sensible ML’s Model Arena automatically selects the most accurate ML model for every product-location combination within differing business units. Ultimately, then, Sensible ML equips Finance professionals with deeper insights into future financial scenarios, enabling better decision-making and strategic planning.
Conclusion
As AI continues to evolve, the impact on enterprise Finance will only further intensify. AI will continue revolutionizing traditional practices and unlocking new opportunities for growth and innovation. From predictive analytics to process automation and risk management, AI empowers enterprises to navigate complex financial challenges with confidence and agility. Finance professionals who use OneStream’s Sensible ML solution can thus unlock the full potential of AI to drive sustainable business success in the digital era.
Learn More
Want to learn more use cases of AI in enterprise Finance for FP&A teams? Stay tuned for additional posts from our Sensible ML blog series, or download our white paper here.
Download the White PaperThe transition from on-premise deployments of enterprise software to the cloud has been in process for the past 10+ years, and now many organizations are embarking on moving their ERP and EPM systems to the latest cloud-based offerings. To sweeten the offer, several of the mega-ERP vendors, including SAP and Oracle, are often bundling their cloud enterprise performance management (EPM) applications for free as part of the ERP upgrade.
While this may sound attractive on the surface, there are several issues to consider here, including the hidden costs associated with “free EPM software.”
Business Value vs. Vendor Lock-In for Free EPM Software
Let’s face it, ERP upgrades are an expensive and risky proposition when you consider the time, resources and costs involved in such an undertaking. So to entice existing customers to stay the course and migrate to their cloud ERP offerings, it seems like a nice gesture for an ERP vendor like SAP or Oracle to bundle in their EPM applications for no charge, effectively discounting them to zero.
What applications am I referring to? I’m referring to EPM software products that handle complex tasks such as financial close and consolidation, budgeting, planning, forecasting, financial and management reporting, and operational analytics.
These EPM modules support critical Finance processes, so buyers should really question the value these free offerings may provide. Here are some questions buyers should be asking about this type of offer:
- Does the free EPM software meet my business requirements? Are all the modules and capabilities you’ll need part of the “free” offering? How many user licenses are included?
- How do the ERP vendors’ EPM software products compare to best of breed solutions that are available in the market?
- Can the Finance team support and maintain these applications or will IT need to support them?
- What will be the time, effort and costs for implementation and support of the EPM applications? What level of value will this deliver to the enterprise?
- Does the implementation of the EPM modules need to wait until after the ERP upgrade is complete, or can they be implemented in advance?
- Does the bundled EPM software integrate with multiple ERPs and other operational systems that are running across the enterprise?
- Is the ERP vendor willing to offer up live reference customers who are using its EPM applications? Do these references have the same business requirements as your organization?
EPM Software Sourcing Preferences
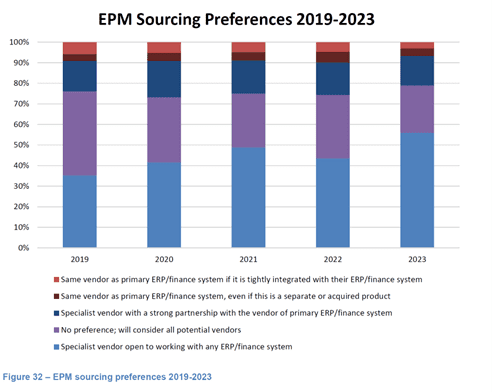
This practice of ERP vendors bundling EPM applications into an ERP purchase or upgrade isn’t something that’s entirely new, this practice has been positioned by the mega-vendors for several years. However, recent surveys of EPM software buyers reveal a strong preference for best of breed EPM solutions vs. those that are provided by ERP vendors. In fact, according to the 2023 Dresner Advisory Wisdom of Crowds™ EPM Market Study, 56% of buyers prefer to source their EPM solutions from a “specialist vendor open to working with any ERP/finance system” and roughly 23% said they had no preference; will consider all potential vendors.
As you can see in the chart below, this preference towards sourcing EPM solutions from specialist EPM vendors has grown since 2019, while the preference to sourcing EPM solutions from the same vendor as the primary ERP/Financial system has shrunk to less than 7% in 2023.
OneStream Extends ERP Investments
At OneStream we work with Finance and IT buyers every day, around the globe, who are evaluating their EPM software options as they contemplate or work through ERP upgrades. And in most of these evaluations, organizations are opting to select OneStream as their EPM software platform of choice. The main reasons for selecting OneStream over their ERP vendor include the following:
- Market-leading EPM functionality in a unified platform.
- High scalability and performance designed to address the world’s largest, and complex global enterprises.
- Ability to integrate data from multiple ERP, HCM, CRM and other source systems including direct integration with over 250 systems including SAP ECC, S/4 HANA, Oracle Fusion, Oracle EBS, PeopleSoft, JD Edwards, Netsuite, Microsoft Dynamics, Infor, Salesforce, Workday and many others.
- Finance ownership for maintenance and support, less dependance on IT.
- Rapid time to value and lower cost of ownership vs. fragmented, multi-product EPM solutions.
- Single source of the truth and improved insights into financial and operational data across the enterprise.
- Flexibility and agility to support the integration of new data sources based on mergers, acquisitions, and divestitures.
Here’s one example of an organization that has adopted OneStream to extend their ERP investments and the value they have achieved.

Costco Wholesale – As a global retailer with over 800 warehouses around the world, Costco was running their financial consolidation, reporting and budgeting processes using multiple SAP and I-Series ERPs, Oracle Hyperion Financial Management (HFM), Excel, and Cognos BI.
Their outdated HFM application and reliance on Excel and complex data movements made it increasingly difficult to maintain the organization’s 1.5-day financial close process. Reporting was highly manual and Excel-based, with over 40 Excel sheets for internal reporting and another 50 for external reporting, creating layers of complexity and painful review and analysis processes. So, the Business and Finance teams began looking at their alternatives and landed on OneStream.
While there was initial preference for selecting an SAP-based reporting and planning solution, stakeholders evaluated OneStream vs. SAP BPC and felt that OneStream better met our business requirements and offered more flexibility.”
With the OneStream project completed, Costco now has a single system of record for close and consolidation, P&L reporting, variance commentary, budgeting, task management and workflow for warehouse and corporate users. The accounting and finance teams now have one place to see all their financial data, spending more time on financial statement review and less time on manual creation and review work.
Learn More
Costco is just one example among many customers who have selected OneStream to extend their ERP investments. In fact, over 400 SAP ERP customers have selected OneStream for EPM, as well as almost 500 Oracle ERP customers. If your organization is considering an ERP upgrade and the mega-vendor is proposing to provide their EPM solution at no cost, make sure to fully evaluate the offering vs. alternatives that may be available in the market and make an informed decision. To learn more check out our OneStream for SAP Customers e-book or contact OneStream for an overview and demonstration of our Intelligent Finance Platform.
Download the eBookToday, all organisations require robust systems and processes across all levels to drive performance improvement, achieve operational excellence and sustain competitive advantage in the dynamic environments they operate.
EPM software forms a management layer above all transaction systems providing a level of agility and visibility now critical for any organisation that wants to successfully handle the non-forgiving complexities of growth and change. With an effective management layer in place, organisations can upgrade or replace underlying ERP/GL systems. And it can be done without disrupting critical management processes, such as planning and reporting, during the transition period.
In this blog post, we review the 5 best EPM software solutions for 2024 using our own interpretation of their relative offerings. We only included software that meets the following non-negotiable qualifications:
- Must be present in the Dresner EPM Market Study 2023.
- Earned at least 4.3/5.0 stars on Gartner Peer reviews for either Planning or Financial Close & Consolidation.
- Software offering includes full management of enterprise-wide consolidation, close, financial and operational planning & forecasting.
What is EPM software?
EPM Software solutions are designed to help organisations effectively manage and analyze their performance data to achieve the strategic objectives they have set. An EPM solution integrates and analyzes data from many sources, including, but not limited to, ERP systems, HCM, CRM, and Supply Chain applications, data warehouses, and also cloud and external data sources. The typical management processes included in EPM solutions are: Goal Setting, Modelling, Planning, Financial Close & Consolidation, Reporting, and Analysis.
EPM solutions typically include the following capabilities:
- Planning, Budgeting & Forecasting
- Close & Consolidation
- Account Reconciliations and Transaction Matching
- Compliance & Regulatory Reporting
- Predictive Modelling & Analytics
- AI Financial Forecasting
Ultimately, EPM software provides management with data analytics and insights across multiple operational systems and processes. EPM solutions provide agility in forecasting and strategic planning, reporting, and decision-making. And they help organizations create alignment across the enterprise.
This comparative analysis explores the features and functionalities of 5 leading EPM solutions: OneStream, Oracle EPM Cloud, SAP EPM, Workday Adaptive & Wolters Kluwer CCH Tagetik.
1. OneStream
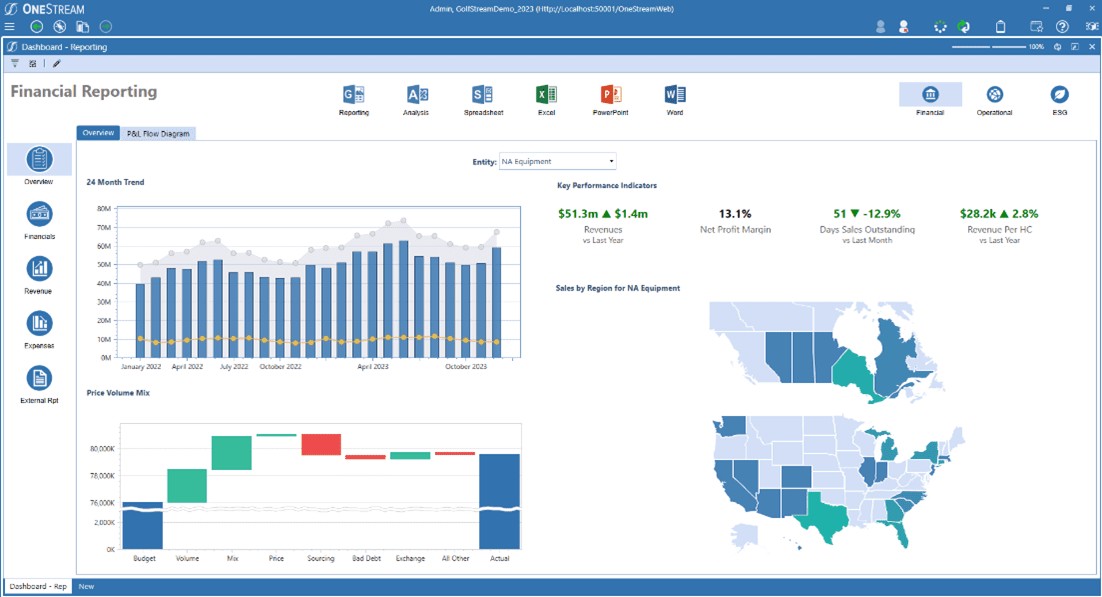
OneStream is the only solution for EPM delivering end-to-end management of enterprise-wide consolidation, close, financial and operational planning & forecasting in a unified platform. This unified platform helps finance, and operations teams collaborate by creating a single source of truth that eliminates the complexity of multiple solutions, interfaces and integrations, cost and duplication of data and metadata, time-consuming processes, and upgrades.
With a built-in data quality engine and pre-built connectors, finance is in control, providing a strong, flexible foundation in data quality that’s ERP and source system agnostic, as real-time as needed, with drill down and drill back to any source, providing auditability across all close, planning, reporting and analysis processes and actionable insights behind every number.
Pros:
- One uniquely unified EPM solution owned by finance for end-to-end management of enterprise-wide consolidation, close, financial and operational planning & forecasting, reporting & analysis.
- Built in data quality engine, providing a strong flexible foundation in integration and data quality delivering confidence, trust and finally, a real one source of truth.
- Built-in self-service reporting, dashboarding, adhoc analysis and deep integration with Microsoft Office in one platform, from balance to transactional details with seamless drill down and drill back to supporting details for transparency, auditability, and actionable details behind every number.
Cons:
- Best for enterprises looking for end-to-end management of enterprise-wide consolidation, close, financial and operational planning & forecasting, reporting and analysis in a unified platform.
- Small to medium size organizations not looking for this unification, while OneStream is user-friendly, mastering the design and advanced features may pose a slight learning curve for these organizations.
- Despite growing popularity, 100% customer success of over 1400+ customers, OneStream may have a smaller but growing market presence compared to a few other alternatives.
2. Oracle EPM
Oracle EPM is a suite of business applications designed for end-to-end management of enterprise-wide consolidation, close, financial planning & forecasting and performance reporting. Oracle is similar to SAP, with legacy solutions from their acquisition of Hyperion with end of support in 2035 for Hyperion HFM and Hyperion Planning. Their suite of applications is being redeveloped on the Cloud, consisting of individual best of breed solutions for each core management process.
Pros:
- A comprehensive suite covering budgeting, planning, forecasting, and advanced analytics, providing the breadth of capabilities for EPM and are well known based on the reputation of Hyperion Solutions
- Integration with Oracle solutions (ERP, HCM, CRM…) and databases, and a robust solution for master data management, data integration and data quality
- A large customer base and global network ensure access to a pool of skilled professionals, services, partners and domain expertise.
Cons:
- Lack of parity in Consolidation & Close solution for consolidation capabilities exists compared to Oracle’s legacy Hyperion HFM solution.
- Fragmented, multiple solutions require multiple complex integrations across solutions to reconcile actuals with plans and to bring in financial and operational data to support the end-to-end consolidation, close, financial, and operational planning, and reporting processes.
- Limited live references and few peer reviews/insights are available for the cloud EPM solutions.
3. SAP EPM
With the end of support of SAP’s legacy EPM solutions – BPC and BFC (BusinessObjects Financial Consolidation) set for 2030, SAP’s go forward solutions for EPM are a combination of SAP Group Reporting embedded in S/4HANA for consolidations and SAP Analytics Cloud for financial and operational planning.
SAP S4/HANA Group Reporting is an enterprise solution for consolidations and since it is part of S4HANA, it leverages a combination of features of Group Reporting for consolidations and S/4HANA for core close capabilities. SAP Analytics Cloud is a cloud-based platform for planning, business intelligence (BI), and predictive analytics, enabling organizations to visualize, plan, and make data-driven decisions.
Pros:
- Both solutions run on the same S/4HANA technology to streamline integration with SAP ERP systems, making it an ideal choice for organizations deeply embedded in the SAP ecosystem.
- SAC offers flexibility in modeling and reporting, catering to diverse business needs.
- SAP customers benefit from SAP’s global footprint, ensuring access to a vast pool of skilled professionals and SAP domain knowledge.
Cons:
- Customers will need to move to S4/HANA and upgrades can be challenging with known impacts on the agility Finance needs to change to Group Reporting for close and consolidation processes.
- Although both Group Reporting and SAC are on S4/HANA, they are still separate solutions, technologies and tools that need to be implemented, integrated, and maintained.
- Requires multiple complex integrations across solutions to reconcile actuals with plans and to bring in non-SAP financial and operational data to support the end-to-end consolidation, close, financial and operational planning, and reporting processes.
4. Workday Adaptive Planning and Consolidation
Workday Adaptive Insight was founded in 2003 as a planning solution with limited consolidation capabilities and acquired by Workday in 2018. It was rebranded initially as Adaptive Planning, but it is now being marketed as Adaptive Planning and Consolidation.
Workday Adaptive Planning covers planning, consolidation, analytics and reporting functions and is built on a proprietary In-memory database enabling collaboration and real time updates in a browser user interface similar to that of a spreadsheet and supports integration of data from ERP and other source systems.
Pros:
- Similar to SAP and Oracle, Workday offers a full stack ERP, Human Capital Management, Peakon Employee Voice, Strategic Source and Adaptive Planning for business process support and CPM/EPM
- End-to-end financial planning process support, covering budgeting, forecasting and strategic planning.
- Intuitive and user-friendly interface, reducing the learning curve for users and facilitating easier adoption across different departments.
Cons:
- Best known as a planning solution, built in consolidation capabilities are weak, especially for complex global consolidations, and limited close capabilities, other than what is built in Workday Financials.
- Fragmented, multiple solutions and technologies require multiple complex integrations across solutions to reconcile actuals with plans and to bring in financial and operational data to support the end-to-end consolidation, close, financial and operational planning, and reporting processes.
- While positioned as a comprehensive set of capabilities, Workday Adaptive has a limited data model for all CPM/EPM processes and has limited data integration capabilities for managing multiple ERP and other source system data integrations needed for all EPM processes.
5. Wolters Kluwer CCH Tagetik
Tagetik was originally developed in 2005 to deliver trusted, comprehensive and scalable CPM solutions globally and was acquired by Wolters Kluwer in 2017. CCH Tagetik is marketed as an end-to-end financial close and consolidation solution for group and entity controllers. It is comprised of multiple solutions for financial consolidation and close, account reconciliation and transaction matching, financial and management reporting, disclosure management (via a partnership with CoreFiling), and ESG & sustainability performance management. It is available in both on-premise and cloud.
Of all the vendors in this article, they appear on the surface as the closest vendor to OneStream’s unified platform, but it’s not until you get into the details of how the solutions work together, that it becomes clear it still suffers from some of the same integration and solution complexities as the multiple application approaches of other vendors in the CPM/EPM market.
Pros:
- Better platform approach then other multi-solution approaches like SAP and Oracle, in the CPM/EPM market
- Prebuilt connectors for SAP and SAP S/4HANA and a data quality engine to integrate with ERPs and other data sources, both financial and operational
- Ability to combine balance and transactional data in the platform.
Cons:
- Limited to one cube/model per application, affecting performance, scalability and in most implementations, results in the need to create multiple applications to support CPM/EPM processes – resulting in the same integration and solution complexities as the multiple application approach of other vendors in this article.
- Limitations on data quality, assurance and drill back, resulting in additional steps, time and manual processes to resolve data issues, with no transparency to drill back to source.
- The customer base is strongest in Europe but lacks the footprint in North America of other vendors in this article.
Conclusion
Choosing the right EPM Software is essential for organizations seeking to move away from unreliable, inadequate EPM applications and/or spreadsheets and to instead evolve to a modern EPM solution.
Each of the Top 5 solutions featured in this blog post offers unique features and benefits, catering to the diverse needs of organizations across industries. Ultimately, however, if you’re looking to streamline your key Finance processes and significantly increase confidence in your reporting, OneStream is the best EPM software to handle all your requirements, no matter how complex.
Learn More
To learn more about how organizations are managing the complexity in their EPM processes, check out our whitepaper titled: Taking Performance Management to the Next Level with Intelligent Finance
And if you’re ready to take the leap from spreadsheets or legacy EPM solutions and start your Finance Transformation with OneStream, let’s chat!
Download the White PaperToday, the corporate budget planning process is vital for Finance. Through this structured approach, organizations allocate resources, forecast financial outcomes and plan for future financial performance. Those key uses underscore why the process is so crucial to effective strategic management.
Corporate Budget Planning
In essence, corporate budget planning enables businesses to align their spending and investment with their goals, priorities and market conditions.
The process typically involves 10 key but straightforward steps.
1. Define Objectives and Strategy
Defining objectives and strategy for corporate budget planning involves setting clear, actionable goals that align with the organization’s broader strategic vision. These objectives, in turn, serve as benchmarks for what the company aims to achieve financially within a specific time period. What aims? A few examples include increasing revenue by a certain percentage, reducing operational costs, expanding into new markets or enhancing capital investment returns.
At the same time, effective objectives are both ambitious and realistic. They provide a focused direction for financial planning and decision-making. Accordingly, the objectives should be developed through a collaborative process that involves input from key stakeholders across the organization. Such input ensures alignment with overall business goals and accounts for the company’s operational capabilities, market conditions and competitive landscape.
The strategy for achieving these objectives is the roadmap that outlines how the organization will allocate resources to meet its financial goals. What’s involved in that strategy? Key elements are detailed planning on revenue generation tactics, cost management initiatives, investment in growth opportunities and risk mitigation measures.
This strategic planning requires a deep understanding of the business environment, including customer demand, economic trends and regulatory changes. That understanding allows for making informed decisions on spending, saving and investing. But whatever the strategy, it should be flexible enough to allow for adjustments in response to unforeseen challenges or opportunities.
Ultimately, the combination of well-defined objectives and a robust strategy enables a company to efficiently execute its corporate budget planning. And that matters because it ensures financial stability and supports long-term organizational growth.
2. Review Past Performance
Reviewing past performance is an essential phase in the corporate budget planning process.
That review acts as a mirror to reflect the organization’s financial health and operational efficiency over previous periods. Thus, this retrospective analysis involves a comprehensive examination of financial statements (e.g., income statements, balance sheets and cash flow statements) alongside operational metrics.
The goal? To identify patterns, trends and anomalies that can inform future budgeting decisions. By understanding where the company has had financial success and faced challenges, leadership can make more informed predictions and decisions for the future. (We believe that Finance teams using AI and Sensible ML to identify patterns, trends and anomalies are the ones getting the farthest ahead.)
Yet this review process goes beyond merely looking at numbers. Instead, it requires a deep dive into the reasons behind those numbers. If the company experienced a significant variance in actual revenues compared to budgeted revenues in a recent FP&A report, for example, knowing the why behind that variance is vital. Was it due to changing market conditions, a new competitor entering the market or perhaps internal factors such as production issues?
Similarly, analyzing expenditure trends helps identify areas of inefficiency or overspending. This analysis can involve examining costs line by line to see where the budget was exceeded and why. Through that process, companies can identify opportunities for cost savings or process improvements.
Reviewing past performance, however, is not just about identifying what went wrong. The process also helps organizations recognize what went right. Why does that matter? Well, success in certain areas – such as a particularly effective marketing campaign or a cost-saving initiative – provide valuable lessons. Those lessons can then be replicated and built upon in future periods.
This phase of the budget planning process also encourages a culture of accountability and continuous improvement within the organization. Essentially, by closely examining past performance, departments and teams can:
- Set more realistic goals
- Better align strategies with corporate objectives
- Adjust plans based on what has been proven to work or not work in the past
Ultimately, in the corporate budget planning process, reviewing past performance is a critical step. It lays the groundwork for more accurate and effective budget planning. In fact, this step ensures the budgeting process is grounded in reality – one where strategies and objectives are informed by empirical data and historical context. This grounding helps organizations not only set more achievable financial targets but also devise strategic initiatives more likely to drive the organization toward its long-term goals.
3. Revenue Forecasting
Revenue forecasting allows a company to estimate its future sales and income over a specified period. What so crucial about this projection? It helps with setting financial targets, making informed decisions about expenditures and planning for growth.
Typically, revenue forecasts are based on a combination of historical sales data, market analysis and an assessment of external factors that could influence demand. Those factors can include economic trends, industry developments and competitive dynamics. By analyzing these elements, companies aim to predict their financial inflow with a reasonable degree of accuracy. And they do it while adjusting for seasonality, market shifts and other variables that might impact revenue.
Effective revenue forecasting requires a meticulous approach – one that blends quantitative analysis with qualitative insights. Companies often use models that incorporate past performance trends while adjusting for future market expectations and strategic initiatives, such as product launches or expansions.
Whatever the model, the forecasting process is inherently iterative, with forecasts regularly updated to reflect new information or changes in the business environment. This dynamic approach allows companies to remain agile. How? It empowers companies to make strategic adjustments to operations, marketing and budget allocations in response to evolving forecasts.
Ultimately, accurate revenue forecasting is essential for strategic planning, resource allocation and financial management. Businesses can use the forecasts to set realistic goals and measure progress toward achieving them.
4. Cost and Expense Estimation
Cost and expense estimation is essential for creating a realistic and effective corporate budget plan. Why, exactly? Such estimations help businesses anticipate financial outflows and manage resources efficiently. For any cost estimation, both fixed and variable costs matter. Salaries, rent and utilities are examples of fixed costs – which, by nature, do not change with the level of goods or services produced. Meanwhile, materials, shipping and commissions are example variable costs, which inherently fluctuate with business activity levels.
The accuracy of cost and expense estimation greatly impacts the ability to maintain profitability and cash flow. To estimate costs effectively, companies analyze historical spending trends to forecast future expenses. This analysis is supplemented with information about planned initiatives, expansion efforts or any operational strategy changes that could affect costs. For variable costs, companies also consider projected sales volumes, pricing strategies, supply chain dynamics and other factors that affect the cost of goods sold and operational expenses.
In addition, effective cost and expense estimation requires a forward-looking approach that considers external factors. Market trends, economic conditions and regulatory changes are just a few of such factors. For instance, anticipated increases in raw material costs, changes in labor laws or fluctuations in currency exchange rates can all impact future expenses. Such considerations enable businesses to develop more accurate and resilient budgets.
But companies must also maintain a degree of flexibility in those budgets to accommodate unexpected costs. This accommodation, in turn, ensures companies can respond to unforeseen challenges – without compromising financial stability.
Overall, cost and expense estimations are not just about predicting numbers. This step is also about understanding the financial implications of a company’s operational and strategic decisions. By carefully analyzing both internal and external factors that influence costs, businesses can create budgets that support their goals while effectively managing risk. This process requires the following:
- Collaboration across departments
- Clear communication of financial goals and constraints
- Regular review and adjustment of estimates to reflect new information or changing conditions
Ultimately, through diligent cost and expense estimation, companies lay the groundwork for financial health, strategic growth, and long-term success in corporate budget planning.
5. Capital Budgeting
Capital budgeting in corporate budget planning is a strategic process that helps companies evaluate and prioritize investments in long-term assets and projects. How? Assessments look at potential expenditures on assets (e.g., new machinery, property, technology upgrades or expansion projects), which require substantial upfront investment but generate returns over several years. Accordingly, the capital budgeting process helps determine which projects align with strategic objectives and offer the best potential for financial return.
Capital budgeting employs various analytical techniques, such as net present value (NPV), internal rate of return (IRR) and payback period calculations. Using these techniques, companies evaluate the profitability and risk of investment proposals. This meticulous evaluation, in turn, helps ensure a company allocates its limited resources to the projects most likely to enhance its competitive position and shareholder value over the long term.
Yet capital budgeting is not merely about identifying and investing in profitable ventures. It also involves strategic planning and risk management. Thus, capital budgeting requires a forward-looking perspective that considers how investments might impact the company’s financial health and ability to respond to future market changes. By carefully selecting projects that contribute to strategic goals (e.g., expanding market reach, improving efficiency or innovating product offerings), companies can sustain growth and adapt to evolving industry landscapes.
Ultimately, this process demands cross-functional collaboration. That collaboration involves input from various departments to ensure projects are feasible, strategically aligned and have a clear implementation plan. Through effective capital budgeting, businesses position themselves to make informed decisions that drive long-term success and resilience.
6. Allocate Resources
Allocating resources in corporate budget planning requires distributing financial assets among various departments, projects and initiatives to achieve strategic goals and operational efficiency. Through this critical step, companies decide how much funding to allocate to different areas of the business. Based on what? The strategic importance, the expected return on investment and the alignment with the company’s overall objectives.
Thus, allocating resources requires a delicate balance between supporting existing operations, investing in growth opportunities and maintaining financial health. Effective resource allocation ensures that every dollar spent contributes to the company’s long-term success. Whether through driving revenue growth, enhancing productivity or entering new markets, those contributions all matter to the company’s bottom line.
Effective resource allocation demands thorough analysis and strategic thinking. To get started, companies must clearly understand its priorities and objectives. A detailed evaluation of the potential impact and costs tied to each budget request is also important. Throughout the process, decision-makers must consider projected revenue, cost savings, market trends, competitive dynamics and other factors. Yet the process isn’t static. It requires continuous monitoring and adjustment in response to performance data and changing market conditions.
Ultimately, companies must regularly review how resources are allocated and make data-driven adjustments. By doing so, companies can invest in the right areas to support sustainable growth and adaptability. This approach thus not only maximizes the return on investment but also strengthens the organization’s ability to navigate uncertainty and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
7. Prepare Budget Drafts
Preparing budget drafts in corporate budget planning is a crucial phase. Preliminary financial plans are developed in this step, reflecting the company’s strategic objectives, revenue forecasts, and resource allocation decisions. This process involves compiling detailed estimates of expected income, expenditures and investments for the upcoming period, usually the next fiscal year.
Drafting the budget requires a collaborative effort across various departments, ensuring each contributes its insights and requirements. This collaborative approach ensures the budget aligns with both the strategic goals of the company and the operational needs of individual departments. In essence, the draft budget serves as a working document – one that facilitates discussions and adjustments before being finalized.
The draft incorporates all the key components of financial planning. What are those components? They include sales forecasts, cost estimates, planned capital expenditures and any other financial commitments. By including these elements, the draft budget provides a comprehensive overview of the company’s financial strategy.
The preparation of budget drafts is iterative, allowing for refinement and adjustment as more accurate or updated information becomes available. That iteration, however, requires a balance between ambition and realism to ensure the budget is challenging but achievable.
In this phase, Finance teams therefore play a pivotal role. How? They analyze data to ensure consistency across different parts of the organization and integrate strategic priorities into the financial planning process. This stage often involves scenario planning and sensitivity analysis to assess the impact of various assumptions and potential risks on the company’s financial performance.
Ultimately, by carefully crafting these budget drafts, companies lay the groundwork for financial discipline, strategic alignment and operational efficiency. The draft budget is therefore a critical tool for guiding decision-making, setting expectations, and providing a baseline against which actual performance can be measured and managed throughout the fiscal year.
8. Review and Approve
In this phase, the draft budget developed through collaborative efforts across departments undergoes scrutiny by senior management and, often, the board of directors. This step ensures the proposed budget aligns with the strategic goals of the organization, remains financially sound, and sets realistic revenue and expenditure targets.
The review process involves a thorough examination of three aspects:
- Assumptions made during the drafting phase
- Validation of the financial forecasts
- Assessment of the proposed resource allocations
Through those aspects, the process offers an opportunity for key decision-makers to challenge and refine the budget. Doing so ensures it supports strategic initiatives, addresses operational needs and effectively manages financial risks.
Notably, this phase may involve several rounds of review and adjustment, with feedback provided to department heads and Finance teams. Why? To further refine the budget until it meets the organization’s strategic and financial objectives. After satisfying the scrutiny of the review phase, the budget moves to the approval stage. This formal endorsement, usually by the company’s top executives and the board of directors, signifies the budget is the official financial plan for the upcoming period.
In other words, the approval process solidifies the organization’s commitment to the budget’s targets and allocations, setting the stage for implementation. The approval also serves as a signal to the entire organization about the priorities and financial direction for the forthcoming period. With that signal, the approval emphasizes accountability and the importance of adhering to the budget.
Ultimately, the approved budget becomes the benchmark against which financial performance is measured, guiding decision-making and financial management throughout the fiscal year. This process of review and approval is crucial for ensuring the budget reflects the collective wisdom and strategic intent of the organization’s leadership. Thus, the process effectively balances ambition with realism and aligns resources with opportunities.
9. Implement the Budget
Implementing the budget in corporate budget planning marks the transition from planning to action. In essence, the approved budget serves as a roadmap for the organization’s financial activities over the upcoming period. This phase involves disseminating the budget details across departments, ensuring that managers and team leaders understand their financial targets and resource allocations.
Implementation requires the following:
- Setting up systems for monitoring expenditures and revenues
- Establishing accountability mechanisms
- Integrating the budget into daily operations and decision-making processes
Effectively taking those actions during implementation ensures all parts of the organization work toward the common financial goals set out in the budget. And everyone does it with a clear understanding of their roles in achieving the targets.
Ultimately, implementing the budget is a continuous process that involves not just following the budget but also adapting to changes. Successful adaptation requires ongoing communication and coordination across the organization to maintain alignment with the overall financial strategy.
10. Monitor and Review
Monitoring and reviewing in corporate budget planning are an ongoing process that involves continuously tracking financial performance against the approved budget throughout the fiscal year. Through this critical step, companies can ensure any deviations from the budget – whether in revenues, expenditures or other financial metrics – are quickly identified. Doing so allows for timely adjustments to stay on track. Collectively, the monitor and review process encompass the following:
- Regular reporting on financial performance
- Analysis of variances
- Assessment of the budget’s effectiveness in supporting the organization’s strategic objectives
Ultimately, the review component allows for reflection on what is driving any discrepancies between actual and budgeted figures. Such reflection leads to insights that inform future budgeting cycles or immediate corrective actions. Through the cyclical process of monitoring and review, companies can foster a culture of financial discipline, promotes accountability across departments. That process thus enhances the organization’s ability to adapt to changing circumstances, thereby ensuring financial stability and strategic alignment.
What’s Next for Corporate Budget Planning?
Don’t forget to reflect on what you learn through every corporate budget planning cycle. Insights gained from monitoring, reporting and adjusting the budget can feed into the next round. In doing so, insights will help your company refine its planning approach and improve accuracy and effectiveness over time.
Want a deep dive into budgeting, planning and forecasting? Check out our free ebook!
Download the eBookMaximizing Success through Corporate Performance Management in the Modern Business Landscape
In today’s competitive business world, achieving optimal performance and driving business success requires a structured approach. Enter Corporate Performance Management (CPM). Across the organization, CPM provides the tools and methodologies to define, measure, monitor and improve performance.
The definition of CPM, its methods and its key performance metrics are crucial knowledge for modern enterprises. In this blog post, we’ll unveil all 3 aspects. We’ll also highlight a few modern examples of organizations that have successfully implemented CPM in different functional areas to achieve desired business outcomes.
Let’s get started by defining precisely what CPM entails.
What Is Corporate Performance Management?
In essence, Corporate Performance Management is a comprehensive approach to managing business performance, encompassing the entire organization. What does that entail? Setting strategic goals, developing plans, budgeting, monitoring, analyzing data and making informed decisions aligned with business objectives are all part of CPM. By adopting a comprehensive CPM approach, organizations can assess overall performance, enhance performance and drive business success.
CPM addresses the following pivotal questions (among others!):
- Are strategic goals being realized?
- How effectively are resources being utilized?
- What areas demand operational enhancement?
- Are stakeholders receiving adequate value?
Methods in Corporate Performance Management
Now let’s dive into 5 key CPM methods that help drive organizational success.
1. Strategic Goal Setting and Planning
Strategic goal setting and planning is a fundamental aspect of CPM. Why? Through this method, an organization articulates its mission, vision and values. Organizations can also establish SMART goals and devise strategic initiatives. Accordingly, this method aligns activities with strategic objectives, ensures efficient resource allocation and maximizes business performance.
An example of this CPM method in action is Virgin Atlantic’s strategic goal-setting and planning:
- Long-term goal: To make Virgin an industry leader in customer service.
- Actions: Developing strategic initiatives (e.g., launching in-flight Wi-Fi, revamping seat designs and improving entertainment systems).
- Outcome: Increased customer satisfaction and improved financial performance.
2. Budgeting, Planning and Forecasting
Budgeting, planning and forecasting together form another essential aspect of CPM. Why? This method involves preparing budgets based on historical data, future projections and strategic goals. By conducting regular monitoring and variance analysis, organizations can identify deviations and take corrective actions. Effective budgeting and forecasting thus contribute to optimal resource allocation and planning.
An example of the budgeting and forecasting method in action is Coca-Cola’s CPM approach:
- Actions: Employing continuous forecasting and performance tracking against KPIs.
- Outcome: Well-informed decision-making, reduced costs and improved sales.
3. Performance Measurement and Reporting
Performance measurement and reporting involves assessing the performance of departments, processes and business units against KPIs to set objectives. How? By employing performance reports, dashboards and scorecards to help not only visualize KPIs, but also identify areas of improvement and those that require attention. Effective performance measurement and reporting drives successful decision-making and performance improvement.
One example of this CPM method in action is Netflix’s performance measurement and reporting:
- Actions: Using performance reports and dashboards to measure organizational performance against subscriber retention, watch time and content quality – all metrics aligned with Netflix’s long-term objectives.
- Outcome: Data-driven decision-making, improved subscriber satisfaction and comprehensive evaluation of organizational performance.
4. Risk Management
Risk management in CPM involves identifying, assessing and mitigating risks that can impact an organization’s performance. How, precisely, is that achieved? The focus is on developing strategies for risk mitigation, conducting risk assessments and monitoring risk indicators. Effective risk management, in turn, contributes to optimal execution and thus reduces the potential negative impacts on performance.
One example of this CPM method in action is Amazon’s risk management strategy:
- Risks to be managed: Supply chain and logistical challenges, as well as concerns about meeting customer satisfaction levels, when launching Amazon Prime.
- Actions: Implementing a proactive risk management strategy.
- Outcome: Identification of potential areas of risk and actions to mitigate those risks.
5. Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement involves evaluating and refining processes to enhance overall efficiency, effectiveness and business outcomes. What does that entail? In short, this method involves adapting to changing environments and aligning tactics with evolving strategic goals. Continuous improvement then drives innovation and enhances organizational competitiveness.
One example of continuous improvement in action is Toyota’s KAIZEN methodology:
- Actions: Engaging in continuous process improvement, emphasizing corporate culture and prioritizing employee involvement.
- Outcome: Fulfilled production demands and improved production quality, making Toyota one of the leading car manufacturers globally.
Key Performance Metrics in Corporate Performance Management
Choosing the appropriate performance metrics is crucial for effective CPM. Why? Well, appropriate and effective KPIs enable organizations to evaluate performance, identify areas of improvement and monitor progress toward goals. Below are some common metrics used in different functional areas.
Financial Metrics
Financial metrics are vital for assessing the profitability, liquidity and overall financial health of an organization. These common financial metrics, among others, are used in CPM:
- Revenue growth: Measures the rate at which revenue is increasing over a specific period to indicate the effectiveness of sales and marketing efforts.
- Gross profit margin: Calculates the percentage of revenue left after deducting the cost of goods sold, with a higher margin indicating better cost management and pricing strategies.
- Operating margin: Reveals the profitability of core operations by measuring the percentage of revenue left after deducting operating expenses, indicating the efficiency of the cost control efforts.
- Return on investment (ROI): Measures the return on investment generated from a particular asset, project or initiative to help evaluate the effectiveness and profitability of investments.
- Cash flow: Assesses the inflow and outflow of cash, with positive cash flow indicating healthy liquidity and good financial stability.
By monitoring these financial metrics, organizations can assess their financial performance, identify areas for improvement and make informed decisions to enhance both profitability and financial stability.
Operational Metrics
Operational metrics evaluate the efficiency and effectiveness of an organization’s core operational processes. Why? Essentially, these metrics provide insights into productivity, quality and resource utilization. The following operational metrics, among others, are used in CPM:
- Cycle time: Measures the time taken to complete a specific process or cycle, helping to identify bottlenecks and areas for process improvement.
- Quality metrics: Assesses the quality of products or services delivered via metrics such as defect rate, customer satisfaction score and product/service, which all reliably provide valuable insights into quality performance.
- Production yield: Determines the percentage of units that meet quality standards during manufacturing, helping to detect inefficiencies and optimize production processes.
- Inventory turnover: Calculates how quickly inventory is sold and replenished, with high turnover indicating efficient inventory management, to minimize risk of inventory obsolescence.
- Supplier performance: Evaluates the effectiveness and reliability of suppliers in meeting quality, delivery and cost requirements, helping to optimize the supply chain and reduce operational risks associated with suppliers.
By using operational metrics, organizations can identify process inefficiencies, improve productivity, enhance quality and optimize resource allocation.
Customer Metrics
Customer metrics focus on measuring and evaluating the organization’s relationship with customers. Why? These metrics ultimately help assess customer satisfaction, loyalty and overall customer experience. Examples of customer metrics used in CPM include the following, among others:
- Customer acquisition rate: Measures the number of new customers acquired during a specific period, indicating the effectiveness of marketing and sales efforts.
- Customer retention rate: Calculates the percentage of existing customers who continue to do business with the organization over a given period, with high customer retention rates indicating customer loyalty and satisfaction.
- Customer satisfaction score: Evaluates customer satisfaction via surveys or feedback mechanisms, helping to identify areas for improvement and ensure customer-centricity.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): Determines customer loyalty and advocacy by measuring the likelihood of customers recommending the organization to others, with a higher NPS indicating stronger customer loyalty and a positive brand image.
By monitoring these customer metrics, organizations can understand customer needs, improve customer satisfaction and strengthen customer loyalty, eventually driving business growth.
Employee Metrics
Employee metrics assess the performance, satisfaction and engagement levels of the organization’s workforce. Why? These metrics play a crucial role in managing talent, fostering a positive work environment and promoting productivity. The following common employee metrics, among others, are used in CPM:
- Employee satisfaction: Measures employee satisfaction and engagement through surveys or feedback mechanisms, helping to identify areas for improvement and assess the effectiveness of HR initiatives.
- Employee turnover rate: Calculates the percentage of employees who leave over a specific period, with high turnover rates potentially indicating underlying issues (e.g., low job satisfaction or ineffective talent management).
- Training hours per employee: Quantifies the investment in employee training and development, helping to assess the organization’s commitment to enhancing employee skills and knowledge.
- Employee productivity: Measures the output or performance of employees in relation to their time and effort, helping to identify high-performing individuals and teams, as well as potential performance gaps.
By tracking and analyzing employee metrics, organizations can make strategic decisions regarding talent management, employee development and overall organizational effectiveness.
Innovation Metrics
Innovation metrics evaluate an organization’s ability to innovate and bring new ideas, products or services to the market. Why? These metrics provide insights into an organization’s innovative capacity and can drive a competitive advantage. Some key innovation metrics used in CPM, among others, include the following:
- Number of new product launches: Measures the number of new products introduced to the market within a specified period, reflecting the organization’s commitment to continuous innovation and ability to generate new revenue streams.
- Research and development investment: Includes the amount of funds allocated to research and development activities, which is essential information for organizations heavily reliant on innovation (e.g., technology companies or pharmaceutical firms).
- Patent filings: Quantifies the number of patents filed by the organization, indicating its ability to protect intellectual property and a commitment to innovation.
By monitoring innovation metrics, organizations can assess their innovation capabilities, identify areas for improvement and foster a culture of continuous innovation.
Conclusion
Ultimately, Corporate Performance Management (CPM) enables organizations to manage performance, align activities with strategic objectives and make informed decisions. With that in mind, here are the key takeaways from this blog post:
- Effective CPM methods (e.g., strategic goal-setting, budgeting and forecasting, performance measurement and reporting, risk management, and continuous improvement) drive organizational success.
- Appropriate KPIs (e.g., financial, operational, customer, employee, and innovation metrics) help manage CPM effectively.
- Success in applying CPM in different functional areas – as shown by Virgin Atlantic, Coca-Cola, Netflix, Amazon and Toyota – helps drive business outcomes and achieve success.
Learn More
For a more in-depth look at CPM in action, check out our Platform webpage – it’s all online, no forms required.
Are you at an enterprise organization looking to upgrade your CPM processes? Get started with a OneStream demo today!
Unlocking the full potential of your organization’s performance hinges on the seamless integration of Corporate Performance Management (CPM) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software. In today’s dynamic business environment, where agility and strategic decision-making are paramount, the synergy between these two essential systems are the backbone to deliver the enhanced visibility organizations need to optimize performance, drive growth and stay resilient in today’s evolving business environment.
ERPs Run the Business – CPM Manages the Business
ERP systems are often thought of as the central nervous system of the enterprise and are essential to the effective execution of day-to-day transactional activities. CPM systems can be thought of as the “brain” of the enterprise, helping to align and coordinate goals, objectives, financial and operational plans and execution across the enterprise. Both systems are critical to the success of an organization. ERP systems are used to run the business, CPM systems are used to manage the business and make critical decisions.
CPM systems source most of their data from internal systems including ERP, but also human capital management (HCM), customer relationship management (CRM) and increasingly external sources such as websites, social media and industry information. And while single-instance ERP has been a goal of many IT organizations, the reality is that most large enterprises have multiple ERPs in use across their various subsidiaries and locations. Therefore, an enterprise-class CPM solution must be capable of integrating and mapping data from multiple ERPs, other source systems and data sources.
Get More Value from SAP Investments with CPM
Many organizations have invested in SAP ERP systems to run their businesses, and SAP data warehouse systems to capture large volumes of transactional data for decision-making. Some have standardized on SAP across all operations, while others run a mixed environment of SAP as well as other ERP systems.
Whatever the case, a unified CPM platform helps organizations get more value from their ERP investments by integrating data from all ERPs and other sources, validating and consolidating that data to create a single source of the truth and “system of record” for consolidating financial results, external financial reporting, internal management reporting, financial and operational planning, analysis and effective decision-making.
Having direct integration to SAP and other ERPs and data sources is critical to having effective and agile reporting and planning processes, and the ability to make fast and informed decisions that can impact corporate performance.
Integrating SAP to OneStream
This was the focus of a webinar hosted by OneStream partner inlumi titled: “All the World’s a Stage – Integrating SAP to OneStream.” The webinar was led by Francisco Amores, MDM and Data Integration Lead at inlumi, who has over 12 years of experience designing and building CPM integration solutions. Here’s a quick summary of the key topics he covered in the webinar.
The webinar started off with an overview of how data is integrated from multiple sources and “staged” in OneStream. OneStream has the ability to integrate data from any source via APIs or Web Services and can also load data via flat files and Excel spreadsheets. Whatever the integration method, it’s in the Stage engine that data is transformed, validated and then loaded into the financial model for processing – whether for financial consolidation, planning, forecasting, and various types of analysis.
In OneStream, data is available to users for reporting and analysis via “cubes” where users can view and analyze summary data, then drill down into the details in the Stage engine, and then drill further back to the original transactional details from the source system.
The webinar then highlighted the key benefits of direct, seamless integration between OneStream and the source systems. These benefits included:
- CPM processes are faster and more reliable – direct integration eliminates manual extraction processes and data latency, reduces the amount of data that needs to be imported and eliminates the need for intermediate data integration tools
- Data Quality, audit and reconciliation – direct integration eliminates the need for manual adjustments on source files and facilitates a direct trace back from the financial model to source systems details
- Helps you to reclaim your life – meaning users don’t have to work as many hours during crunch times such as month-end or quarter-end close and reporting
OneStream leverages several approaches for direct integration with SAP data sources, OneStream connections need to be established only once for ongoing integration with SAP:
- SAP R/3 Version 4.6C and later
- mySAP
- SAP ERP / ECC 5.0 / ECC 6.0 (including all EhPs)
- SAP Business All-in-One
- SAP Business Suite 7
- SAP S/4HANA
- SAP BW 3.1 and later
- SAP BW/BI 7.x
- SAP BW/4HANA
- SAP Application Server ABAP, Message Server, Router, Standalone Gateway
The webinar then provided detailed examples of how several of these integrations are configured and how they work, including HANA ODBC Driver and the SAP Integration Connector. And then the power of OneStream to support “round trip” integration with SAP by loading Profit Center balances from GLPCT were demonstrated, as seen in the graphic below:
Then validating that all imported data was mapped to the target intersections, loading data into the target financial model/cube, drilling down to Stage from reports and dashboards. Then drilling back into the transaction details in SAP GLPCA as shown below.
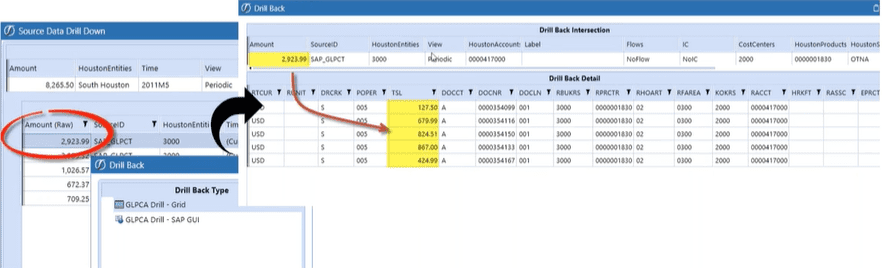
Learn More
This webinar provided a short, but powerful overview and demonstration of the ability OneStream provides organizations to leverage their investments in SAP ERP and data warehouse systems, as well as other data sources. OneStream provides direct and seamless integration to a unified Intelligent Finance Platform that supports consolidations, close, financial and management reporting, financial and operational planning, and reporting and analysis for Finance and line of business users.
To learn more, watch this webinar on how to Unlock Financial Excellence through SAP and OneStream with Avvale and Langan, or check out our eBook on how to Get More From Your SAP Investment.
Download the eBookGovernment Finance leaders today are under pressure to improve decision support, increase transparency and create efficiencies. In addition, agencies are up against the constraints of legacy systems, tedious manual processes and inefficient analytics tools. Agencies thus turn to the best government budgeting software solutions to automate processes and mitigate those challenges. Here, we’ve curated the 5 best budget government software solutions based on their features, customer reviews and industry recognition.
To compile this list, we’ve considered software that meets the following qualifications:
- Earns industry recognition on reputable review platforms such as Gartner Peer Insights
- Offers comprehensive budgeting features for government agencies
- Provides reliable customer support
What Is Government Budgeting Software?
For government agencies, budgeting software plays a pivotal role in the ability to streamline planning processes, increase transparency and gain new insights. Solutions should be tailored to the specific needs of government agencies. How? By encompassing the entire budgeting process from strategic planning, budget formulation, budget execution and performance management to reporting and analytics.
Below are some common features found in budgeting software for government agencies:
- Automation of budget preparation tools
- Robust integration and enterprise data management
- Standard and ad-hoc reporting and dashboard capabilities
- Strong security measures
- Intuitive workflow management
By leveraging these features, agencies can streamline planning processes, minimize errors and make well-informed financial decisions.
Not sure what budget software solution best suits your agency? You’re in the right place!
In the comparative analysis that follows, we’ll explore the features and functionalities of 5 leading government budgeting solutions: OneStream, Oracle EPM Cloud, SAP, Workday/Adaptive and Anaplan.
The Best Budgeting Software Solutions for Government Agencies
1. OneStream
OneStream is a leading enterprise Finance solution trusted by government agencies. It offers a comprehensive platform uniquely unifies financial consolidation, planning, reporting and analysis. With robust budgeting features, OneStream offers the following benefits to government agencies (see Figure 1):
- Unifies all financial and operational data
- Allows agencies to accelerate and simplify planning processes across the Budget and Finance offices
- Embeds AI for better decisions and productivity
OneStream’s unified platform enables Finance and Operations teams to better collaborate and deliver a single source of truth. Having that single source eliminates the complexity of multiple solutions, interfaces and integrations. Not to mention, agencies can also avoid the heavy cost and duplication of data and metadata while avoiding time-consuming processes and upgrades.
OneStream’s unified platform enables Finance and Operations teams to better collaborate and deliver a single source of truth. Having that single source eliminates the complexity of multiple solutions, interfaces and integrations. Not to mention, agencies can also avoid the heavy cost and duplication of data and metadata while avoiding time-consuming processes and upgrades.
Pros:
- Highest customer success rate in the industry.
- Only complete, end-to-end FedRAMP Moderate certified and DoD Impact level 4 (IL-4) provisional authorized cloud CPM provider.
- Intuitive platform with a logical, efficient and modern user experience.
- Comprehensive platform that supports end-to-end PPBE processes for government agencies.
- Ability to support growth and evolution of agencies over time without reimplementing or adding more technical debt.
- Built-in self-service reporting, dashboarding, ad-hoc analysis and deep integration with Microsoft Office in one platform – from balance to transactional details with seamless drill down and drill back to supporting details for transparency, auditability and actionable details behind every number.
Cons:
- Implementation may require additional time and resources.
- Users may face a learning curve during initial implementation.
2. Oracle Enterprise Performance Management Cloud
Oracle Enterprise Performance Management Cloud (Oracle EPM Cloud) provides a solution for federal agencies to automate budget formulation and execution. It offers features for planning, forecasting, reporting, security and workflow capabilities.
Pros:
- Access to a pool of skilled professionals, services, partners and domain expertise thanks to a large customer base and global network.
- Integration with Oracle solutions (ERP, HCM, CRM, etc.) and databases, and a good solution for master data management, data integration and data quality.
- FedRAMP low authorized provider.
Cons:
- Limited live references, footprint and peer reviews/insights for the cloud EPM solutions.
- Multiple fragmented solutions that require multiple complex integrations across solutions to reconcile actuals with plans and bring in financial and operational data to support end-to-end consolidation, close, financial & operational planning, and reporting processes.
- Implementation may require significant time and resources.
3. SAP
SAP’s solution for EPM are a combination of SAP Group Reporting embedded in S/4HANA for consolidations and SAP Analytics Cloud (SAC) for financial and operational planning.
SAP S/4HANA Group Reporting is an enterprise solution for consolidations. As part of S/4HANA, the Group Reporting solution leverages a combination of features tied to Group Reporting for consolidations and S/4HANA for core close capabilities. SAP Analytics Cloud is a cloud-based platform for planning, business intelligence (BI) and predictive analytics that enables organizations to visualize, plan and make data-driven decisions.
Pros:
- Reliance of both solutions on the same S/4HANA technology to streamline integration with SAP ERP systems.
- Global footprint that ensures access to a vast pool of skilled professionals and SAP domain knowledge.
- FedRAMP authorized provider.
Cons:
- Group Reporting and SAC use the same underlying technology, but remain separate solutions with separate implementations and resources.
- Multiple products must be connected and result in disparate data silos. Each product implemented means an additional integration point. Each integration is a point of failure risk due to needing data quality testing and problem resolution, plus on-going maintenance and modifications as requirements change.
- Lack of features, capabilities and flexibility means solutions cannot meet comprehensive and changing requirements of organizations.
4. Workday Adaptive Planning
Workday Adaptive Planning covers planning, consolidation, analytics and reporting functions. Built on a proprietary in-memory database, the solution enables collaboration and real-time updates in a spreadsheet-like browser user interface.
Pros:
- Supports financial planning process support that covers budgeting, forecasting and strategic planning.
- Intuitive interface for users across different departments.
- Easy integration with Workday Finance and HR.
Cons:
- Limited live references, footprint and peer reviews/insights for the cloud EPM solutions.
- Not a FedRAMP authorized provider.
- Fragmented, multiple solutions and technologies that require multiple complex integrations across solutions to reconcile actuals with plans.
- Limited data model for all CPM/EPM processes and limited data integration capabilities for managing the multiple ERP and other source system data integrations.
- Potential learning curve for new users.
5. Anaplan
Anaplan is a cloud modeling technology that enables planning, budgeting and forecasting on a single platform. The solution serves clients in an array of verticals and functions, including Finance, Sales and Marketing, Supply Chain, and HR and Workforce.
Pros:
- User-friendly browser interface.
- Flexible modeling that supports a broad set of planning use cases.
- Professional services team that works alongside its partner network to ensure implementation support.
Cons:
- Limited live references, footprint and peer reviews/insights for the cloud EPM solutions.
- Not a FedRAMP authorized provider.
- Extra time and resources potentially needed to scale and evolve with agency to update and/or connect modules in response to changes.
- Limited financial intelligence in platform, requiring everything to be developed each time.
- Potential learning curve for new users.
Conclusion
Choosing the right budgeting solution is essential for agencies looking to move beyond legacy/manual processes and evolve to a modern EPM solution. In this blog post, each of the 5 best budgeting software solutions highlighted offers unique features and benefits, catering to the diverse needs of government agencies.
However, one financial budgeting software solution stands above the rest if you’re looking to streamline back-office Finance processes and significantly increase confidence in reporting and planning. OneStream ultimately offers the best software to handle your agencies evolving needs, no matter how complex.
Learn More
To learn more about how government agencies are conquering complexity and modernizing back-office processes, click here to check out our customer success with government agencies.
Learn More
